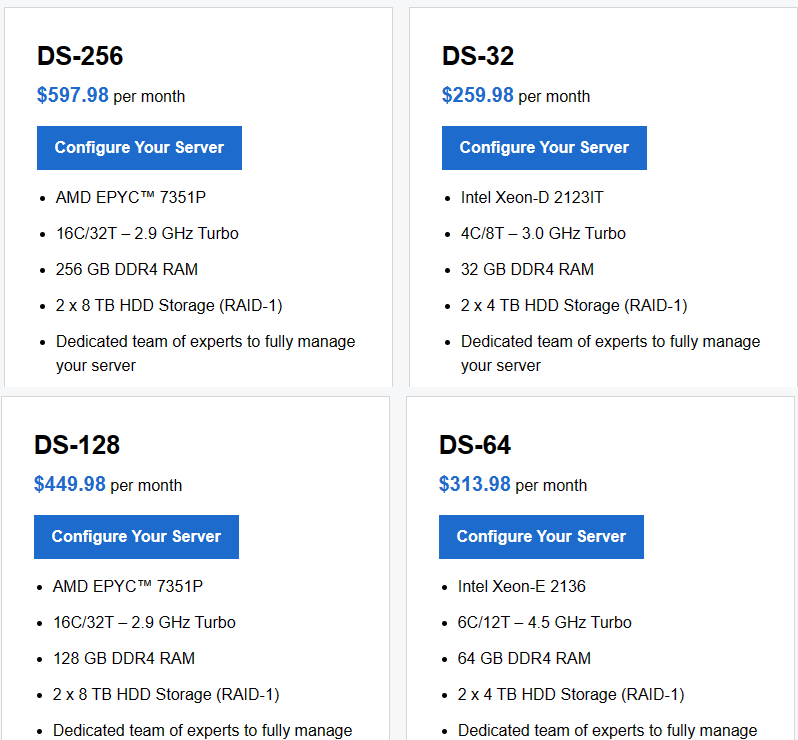
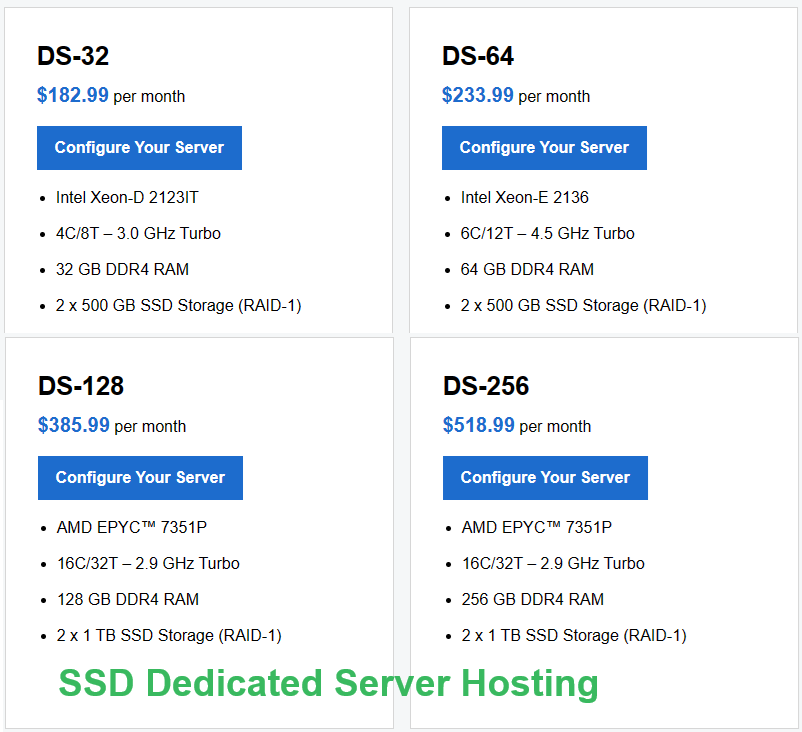
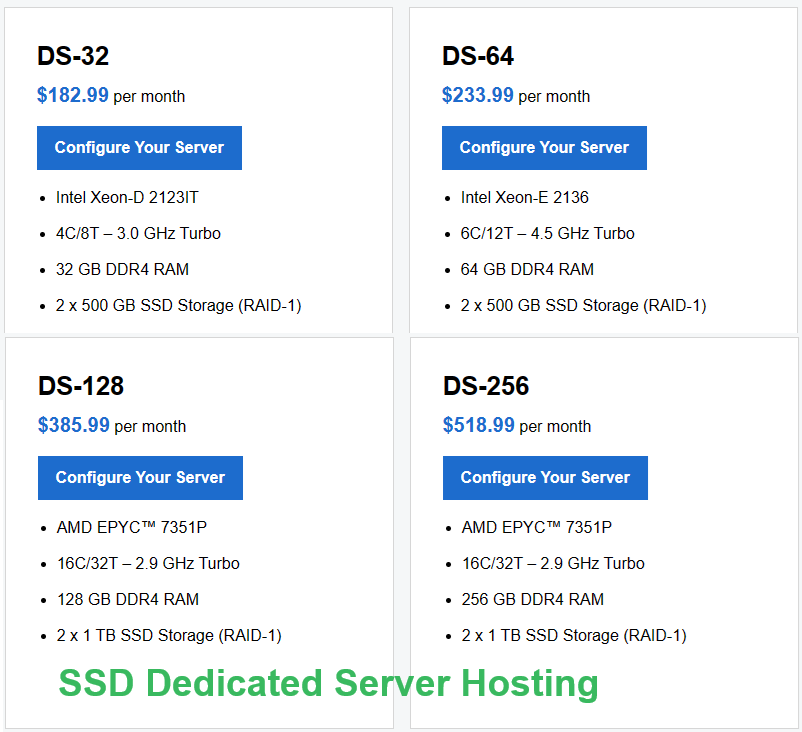
Linux Dedicated Server plan
HDD Dedicated Server
SSD Dedicated Server
What is the Difference Between HDD and SSD ?
- Solid-state drives (SSDs) are the most common storage drives today.
- SSDs are smaller and faster than hard disk drives (HDDs).
- SSDs are noiseless and allow PCs to be thinner and more lightweight.
- Hard disk drives (HDDs) are more common in older devices.
- If you primarily use your PC for web browsing and light work, you may not need as much storage space.
- If you work with large videos or files, you may want more storage.
- If you use OneDrive or another cloud storage service for photos and files, you may need less storage on your device.
HDD (Hard Disk Drive) and SSD (Solid State Drive) are both types of storage devices used in computers, but they have several key differences in terms of their technology, performance, and characteristics:
- Technology:
- HDD: HDDs use magnetic storage technology. They consist of one or more spinning disks (platters) coated with a magnetic material. Data is stored on these platters in the form of magnetic patterns, and read/write heads access the data as the disks spin.
- SSD: SSDs use NAND-based flash memory to store data. They have no moving parts, and data is stored in memory cells. This lack of mechanical components makes SSDs more resistant to physical shocks and faster than HDDs.
- Speed:
- HDD: HDDs are relatively slower compared to SSDs. The speed at which data can be read or written is limited by the spinning disks and mechanical read/write heads.
- SSD: SSDs are much faster than HDDs. They offer faster data access times and transfer speeds because there are no physical components that need to move.
- Durability and Reliability:
- HDD: HDDs are more susceptible to physical damage due to their moving parts. They can be sensitive to shocks, drops, and vibrations.
- SSD: SSDs are more durable because they have no moving parts. They are better equipped to handle physical shocks and are less prone to mechanical failure.
- Noise and Power Consumption:
- HDD: HDDs can generate noise due to the spinning of the disks and movement of the read/write heads. They also tend to consume more power.
- SSD: SSDs are silent since they have no moving parts. They also generally consume less power compared to HDDs.
- Size and Weight:
- HDD: HDDs are usually larger and heavier due to the mechanical components required for operation.
- SSD: SSDs are smaller and lighter as they do not require spinning disks or mechanical components.
- Cost:
- HDD: HDDs are generally less expensive per unit of storage compared to SSDs.
- SSD: SSDs are more expensive, but prices have been decreasing over time as the technology becomes more widespread.
In summary, SSDs offer faster performance, better durability, and energy efficiency compared to HDDs, but they are typically more expensive on a per-gigabyte basis. HDDs are still widely used for large-scale storage needs where cost is a primary consideration, while SSDs are preferred for tasks that demand speed, such as operating system installations and applications that require quick data access.
Linux Dedicated Server Features
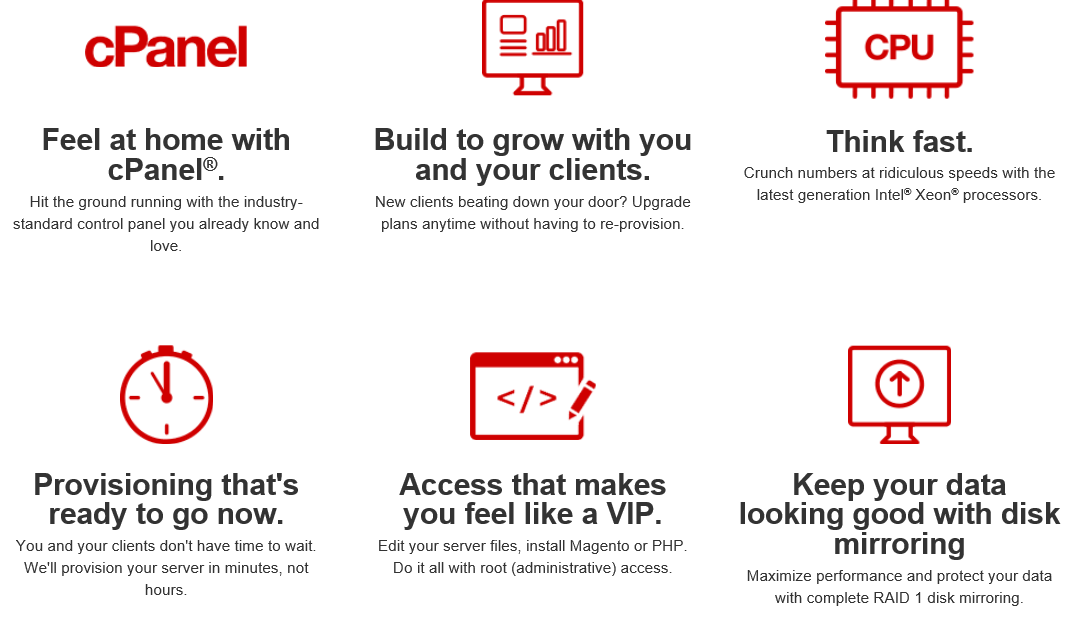 We also Provide Fully Managed Linux WHM/cPanel Dedicated Server
We also Provide Fully Managed Linux WHM/cPanel Dedicated Server
Fully Managed HDD WHM/cPanel Dedicated Server
Fully Managed SSD WHM/cPanel Dedicated Server
Levels of Management of Dedicated Serverx Server?
We provide All following features
- Feel at home with cPanel®. Hit the ground running with the industry-standard control panel you already know and love.
- Built to grow with you and your clients. New clients beating down your door? Upgrade plans at anytime without having re-provision.
- Think fast.Crunch numbers at ridiculous speeds with the latest generation Intel® Xeon® processors.
- Keep your data looking good- with disk mirroring.You’re in charge with root (administrative) access to install PHP, modules, server level proxy, and much more.
- Provisioning that’s ready to go now. You and your clients don’t have time to wait. We’ll provision your server in minutes, not hours.
- Access that makes you feel like a VIP.Edit your server files, install Magento or PHP. Do it all with root (administrative) access.
- Never lose your work again.Travel back in time (kind of) to reclaim lost files with Site Backup. Just C$7.99 for 50 GB (optional).
- Need MySQL? You got it.What server would be complete without the world’s most popular open source database? Not ours, that’s for sure. Get MySQL with all of our Linux server plans.
Our servers (both VPS and dedicated) come in three flavors, depending on the support and features you need:
Self Managed Servers are for the pros among us who want as much control as possible. These are great if you’re comfortable with shell prompts and are a seasoned administrator.
Managed Servers were created with most customers in mind. They offer the power of a server, as well as the ease of managing your server through a control panel. However, it’s still significantly more complicated than something like a WYSIWYG program like Website Builder.
Fully Managed Servers give PowerHoster the responsibility of managing and maintaining your server. You’re still responsible for the sites you want to host on the server, but we take care of pretty much everything else.
Comparing Plans
Here’s a break down of what the above information translates to in terms of this and that.
| Feature | Self Managed | Managed | Fully Managed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automatic Patching | – | ✓ | ✓ |
| Root Access | ✓ | Configurable | Configurable |
| Control Panels | – | ✓ | ✓ |
| Backups: On-Demand | – | ✓ | ✓ |
| Backups: Disaster Recovery | – | ✓ | ✓ |
| SSH | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Application Manager | – | ✓ | ✓ |
| Dedicated IPs | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| Migrations from Shared Hosting | – | ✓ | ✓ |
| Expert Services (ES) | $ | $ | ✓ |
| Monitoring | Good | Better | Best |
| Seamless upgrades | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Support: Chat | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Support: Dedicated Team | – | – | ✓ |
Feature Definitions
Get hip to our lingo…(that’s what the kids say these days, right?)
Patching
When security vulnerabilities are patched, it’s important to get them on your server as soon as possible. Using automatic patching, your server leverages the patching tools available through its operating system or control panel to update potentially problematic elements quickly.
Root Access
To install software on your server through the command line or other administrator-level tasks, you’ll probably need root access. Unless you’re familiar with controlling your server via command line, we don’t recommend using it though; it’s much easier to break your server using the power root access gives you than it is to use the same privileges to fix it.
Control Panels
Manging your server can much more straightforward with a control panel, which creates a user interface to complete administrator-level tasks like creating FTP users and adding websites to your server. Without a control panel, you can only manage your server via command line.
Backups: On-Demand
You’ve seen those warnings where we say, “We recommend backing up your server before making these changes.” This is that backup. Create one backup and restore your server to it if things don’t work out like you anticipated.
Backups: Disaster Recovery
If your server suffers severe breakage, we often have a backup of your server. These restores are available for a fee by contacting customer support.
Warning:We do not guarantee that we will have a Disaster Recovery backup of your server. We make a best effort to keep these available, but you cannot rely on this backup’s availability.
SSH Access
Pros who use servers often find that rather than dealing with a GUI, it’s quicker and easier for them to just issue commands to the server themselves; SSH is the means by which they can do that.
Application Manager
Installing applications like WordPress or Drupal grows increasingly tedious the more often you do it. With an application manager, you’ll have a vast library of apps from which to choose, as well as the tools for features like automatic updates and relocating the application on your server.
Migrations from Shared Hosting
Upgrading from shared hosting to a server has a lot of benefits, but if you were apprehensive about moving your site, our migration tool makes it really easy. With nothing more than a few clicks, we sweep your old shared hosting account up into your server and set everything up for you.
Right now, this feature is available only for cPanel/Linux accounts, but we will add the features for Plesk soon.
Expert Services (ES)
Much like contracting out your home remodeling efforts, our server admins are available to spruce up/patch/overhaul components of your server. We have the entire list available in our Hosting Services Menu.
Monitoring
There are two primary elements we monitor:
- Our network, to ensure it stays healthy and happy, successfully routing your server’s visitors to it.
- Your server’s container, which uses NodePing and other technologies to make sure your server’s successfully responding to requests.
Each of our server support tiers offers a different monitoring system:
Self Managed/Good only includes network monitoring to make sure you’re not getting DDoSed.
Managed/Better includes network and container monitoring so you’ll know if your server ever went down.
Fully Managed/Best includes network and container monitoring, as well as a team of server professionals that will address any issues your monitoring reports.
Seamless Upgrades
If you find that you need a more powerful server, we offer in-place upgrades that require no work on your end.
Support: Chat
Support: Dedicated Team
Our Fully Managed Servers include the kind of white-glove service you expect, including dedicated teams of server admins you can reach out to if you need anything done on your server.
 |
 |
 |
Buy Linux Dedicated Servers at powerhoster.com
What is Webhost Manager, or WHM/cPanel?
WHM/cPanel is a web hosting control panel software suite that provides a graphical interface and automation tools designed to simplify the process of hosting a website. It is used by many web hosting providers to offer a user-friendly platform for both server administrators and end-users.
Here’s a breakdown of WHM (WebHost Manager) and cPanel:
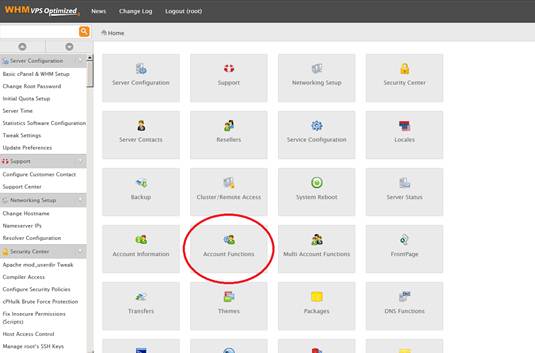
- WHM (WebHost Manager):
- Server Administration: WHM is the backend or server-side component of the software. It is used by hosting providers and system administrators to manage the server as a whole.
- Reseller Hosting: WHM enables hosting providers to create and manage multiple cPanel accounts on the server. This is particularly useful for reseller hosting, where individuals or companies can sell hosting services to their clients.
- Server Configuration: WHM provides tools for configuring server-wide settings, installing software, managing security, and handling other administrative tasks.
- Access to Multiple cPanels: With WHM, you can access and manage all the individual cPanel accounts hosted on a server.
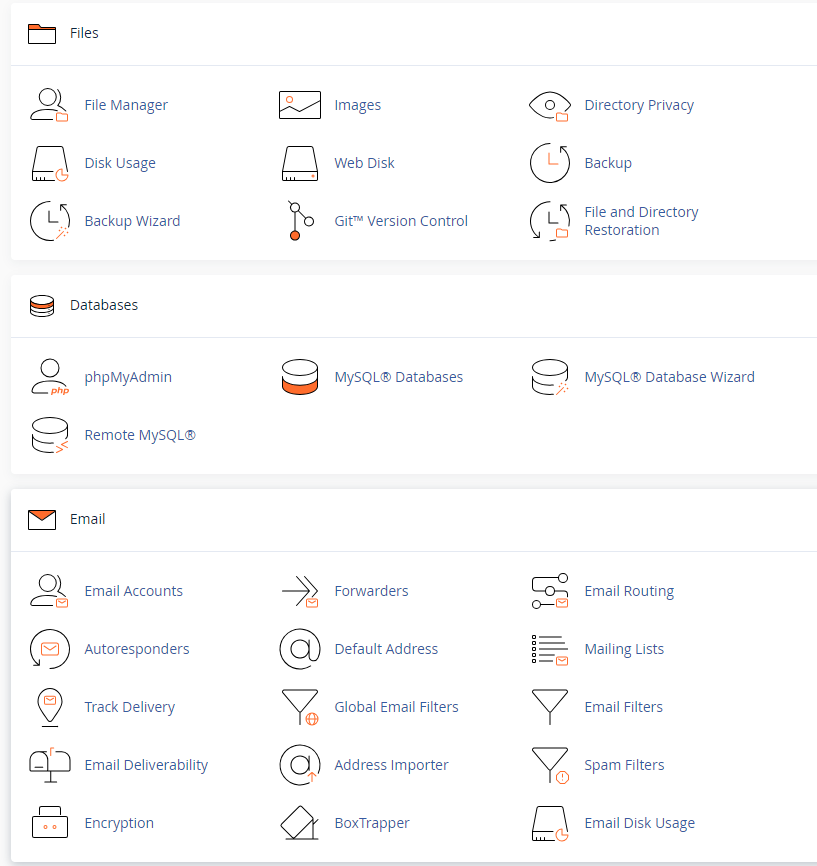
- cPanel:
- User Interface: cPanel is the user-facing side of the control panel. It provides a graphical interface for website owners to manage their individual hosting accounts.
- End-User Functions: cPanel allows users to manage their files, databases, domains, email accounts, security settings, and other aspects of their hosting environment.
- Individual Account Management: Each hosting account has its own cPanel, and users typically access it through a URL like
http://yourdomain.com/cpanel.
Together, WHM and cPanel work in tandem to provide a comprehensive web hosting solution. WHM is used for server administration and managing multiple hosting accounts, while cPanel is used by end-users to manage the specific settings and features of their individual hosting accounts. The combination makes it easy for both administrators and users to handle various aspects of web hosting in a user-friendly manner.
For more information about cPanel and WebHost Manager, visit the cPanel website at http://www.cpanel.net.
What is the Difference Between cPanel and Webhost Manager(WHM)?
WebHost Manager, or WHM, provides administrative control of your dedicated or Virtual Private Server (VPS). You use WebHost Manager to create individual accounts, add domains to your server, manage hosting features, and performing basic system and control panel maintenance.
cPanel is designed for managing particular domains or hosting accounts on your server. End users can control everything from adding/removing email accounts to administering MySQL databases.
cPanel and WebHost Manager (WHM) are two components of a web hosting control panel software suite used by many hosting providers. They work together to provide a user-friendly interface for managing various aspects of web hosting. Here’s a breakdown of the differences between cPanel and WHM:
- cPanel:
- User Interface: cPanel is the user-facing side of the control panel. It provides a graphical interface for website owners to manage their individual hosting accounts.
- End-User Functions: cPanel allows users to manage their files, databases, domains, email accounts, security settings, and other aspects of their hosting environment.
- Individual Account Management: Each hosting account has its own cPanel, and users typically access it through a URL like
http://yourdomain.com/cpanel.
- WHM (WebHost Manager):
- Server Administration: WHM is the server administration interface that sits behind cPanel. It is used by hosting providers and system administrators to manage the server as a whole.
- Reseller Management: WHM allows hosting providers to create and manage multiple cPanel accounts (for different domains or clients). This is particularly useful for reseller hosting, where individuals or companies can sell hosting services to their clients.
- Server Configuration: WHM provides tools for configuring server-wide settings, installing software, managing security, and more.
- Access to Multiple cPanels: With WHM, you can access and manage all the individual cPanel accounts hosted on a server.
In summary, cPanel is the user interface for managing individual hosting accounts, while WHM is the backend system for server administration and managing multiple cPanel accounts. Hosting providers use WHM to create and manage hosting accounts, set server-wide configurations, and handle other administrative tasks. End-users, on the other hand, interact with cPanel to manage their specific hosting account.
For more information about cPanel and WebHost Manager, visit the cPanel website at http://www.cpanel.net.
What Are the Benefits of WHM/cPanel Web Hosting ?
WHM/cPanel web hosting offers several benefits for both hosting providers and end-users. Here are some of the key advantages:
For Hosting Providers (Using WHM):
- Server Management: WHM provides a centralized platform for server administrators to manage and configure the server. This includes tasks such as software installation, security settings, and server resource management.
- Reseller Hosting: WHM facilitates reseller hosting by allowing providers to create and manage multiple cPanel accounts. This is beneficial for individuals or companies that want to sell hosting services to their clients.
- Resource Allocation: Hosting providers can allocate resources such as disk space, bandwidth, and email accounts to individual cPanel accounts, ensuring fair distribution among users.
- Security Features: WHM includes tools for server-wide security configurations, such as firewalls, SSL certificate installations, and other measures to enhance the overall security of the hosting environment.
- Backup and Restore: WHM provides tools for creating and managing backups at the server level. This is crucial for disaster recovery and data protection.
For End-Users (Using cPanel):
- User-Friendly Interface: cPanel offers a user-friendly graphical interface that makes it easy for website owners to manage their hosting accounts without advanced technical knowledge.
- Website Management: Users can manage various aspects of their website, including files, databases, domains, and email accounts through cPanel.
- One-Click Installs: cPanel often includes tools like Softaculous or Fantastico, allowing users to easily install popular web applications, content management systems, and scripts with just a few clicks.
- Email Management: Users can set up and manage email accounts, forwarders, autoresponders, and spam filters through cPanel’s email management tools.
- Security Options: cPanel provides security features such as SSL certificate installation, password-protected directories, and IP blocking to enhance the security of websites.
- Statistics and Analytics: Users can access website statistics and analytics, including information about visitors, bandwidth usage, and error logs.
- Backup and Restore: cPanel allows users to create and restore backups of their website and associated data. This is valuable for safeguarding against data loss.
In summary, WHM/cPanel web hosting offers a convenient and user-friendly environment for both hosting providers and end-users. It streamlines server management, facilitates reseller hosting, enhances security, and provides a range of tools for website management and optimization.
What Are the Benefits of Linux Hosting ?
Linux hosting, as opposed to Windows hosting, comes with several benefits that make it a popular choice for web hosting. Here are some key advantages of Linux hosting:
- Cost-Effective: Linux is an open-source operating system, which means that it is freely available for use. Hosting providers can offer Linux hosting at a lower cost compared to Windows hosting, making it an economical choice for users.
- Open Source Software Compatibility: Many open-source web applications and software, including popular content management systems like WordPress, Drupal, and Joomla, are designed to run on Linux servers. Linux hosting is well-suited for websites built using these technologies.
- Stability and Reliability: Linux is known for its stability and reliability. Linux servers are often chosen for their robust performance and uptime, making them suitable for hosting mission-critical websites.
- Security: Linux is inherently more secure than some other operating systems. It benefits from a strong security model, regular security updates, and a large community of users and developers actively monitoring and addressing potential vulnerabilities.
- Flexibility: Linux hosting supports a wide range of scripting languages, including PHP, Perl, and Python. This flexibility allows developers to choose the best tools for their applications.
- Command Line Control: For users with technical expertise, Linux hosting provides a powerful command-line interface (CLI) for server management. This can be advantageous for tasks that require more granular control over server configurations.
- Scalability: Linux hosting is easily scalable, making it suitable for websites that experience varying levels of traffic. It can handle both small personal websites and large enterprise-level applications.
- Community Support: The Linux community is large and active. This means that there is a wealth of documentation, forums, and community support available for troubleshooting and getting assistance with any issues that may arise.
- Compatibility with LAMP Stack: Linux is a key component of the LAMP (Linux, Apache, MySQL, PHP/Perl/Python) stack, a popular and widely used combination for hosting dynamic websites and web applications.
- Resource Efficiency: Linux generally requires fewer system resources compared to Windows, allowing for efficient use of server resources and improved performance.
It’s important to note that the choice between Linux and Windows hosting depends on the specific needs of your website or application. While Linux is a strong choice for many scenarios, certain applications and development environments may require Windows hosting. Always consider the technical requirements of your website and the technologies you plan to use when selecting a hosting platform.