Protect your site and keep customers safe. Your comprehensive and simplified security solution.
Get the tools you need to help protect your site:
- HTTPS encryption with an SSL.
- Help prevent malware with firewall.
- Detect and fix malware with scanning and remediation.
- Recover your site with 1-click backup.
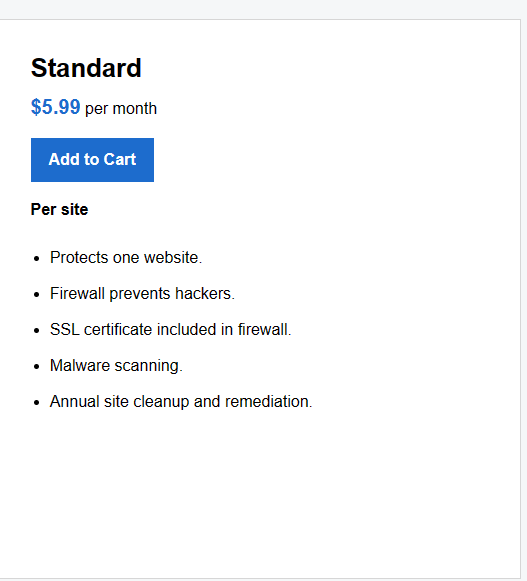
Standard Website Security
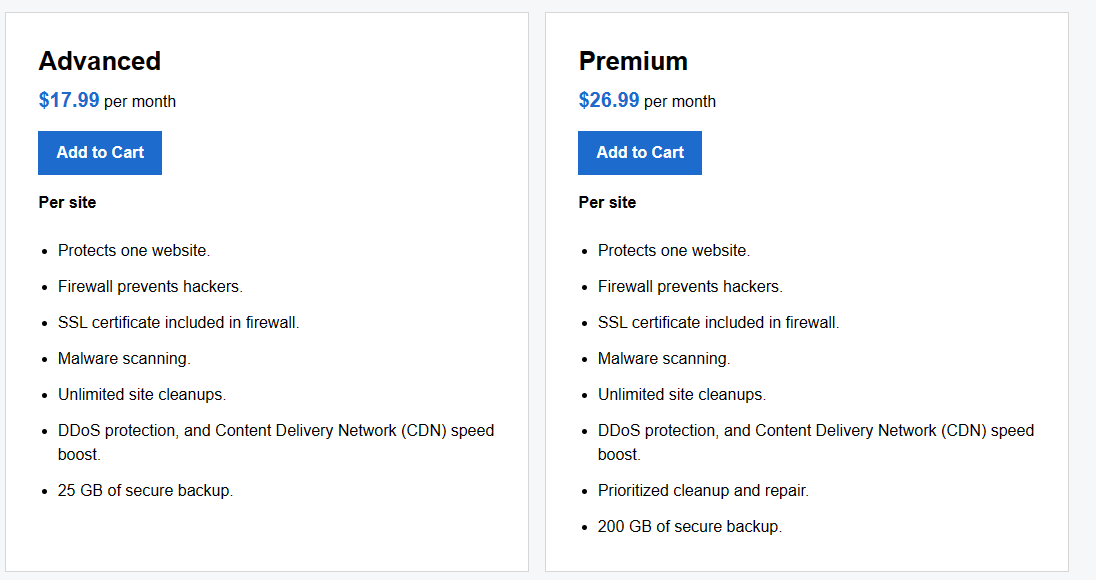
Advanced and Premium Website Security
What’s Website Security?

Website Security provides easy-to-use tools to help protect your site from the most common security threats. After all, your website’s the center of your business, your brand and all the amazing things you’re bringing to the world. It deserves website security tools to help provide broad protection.
Benefits of Website Security
Website security is crucial for various reasons, and implementing robust security measures provides numerous benefits. Here are some key advantages:
- Protecting Sensitive Data:
- Websites often handle sensitive information such as personal details, credit card numbers, and login credentials. Security measures help safeguard this data from unauthorized access and potential misuse. All Website Security plans include an SSL Certificate — which comes with our Web Application Firewall (WAF), allowing your site to provide HTTPS encryption. This lets visitors know that your site’s trustworthy and that any data they exchange with your site is encrypted, keeping it safe from snooping or exploitation.
- Building Trust with Users:
- Users are more likely to trust a website that demonstrates a commitment to security. Implementing security features such as SSL certificates and secure payment gateways helps establish trust with visitors. Our WAF is designed to intercept and examine incoming data and neutralize malicious code from security threats like SQL injections and DDoS attacks. Plus, our Content Delivery Network (CDN) provides even further protection from DDoS attacks by restricting access to your site’s original server.
- Preventing Data Breaches:
- Security breaches can lead to the exposure of confidential information, damaging the reputation of a website or business. Implementing security measures reduces the risk of data breaches and the associated negative consequences.
- Maintaining Website Availability:
- Security measures, such as protection against DDoS attacks, help ensure that your website remains available and accessible to users. This is crucial for maintaining a positive user experience and preventing disruptions.
- Guarding Against Malware:
- Websites can be vulnerable to malware attacks that can infect users’ devices or compromise the integrity of the website itself. Security measures, such as regular malware scans and timely updates, help mitigate these risks.
- Compliance with Regulations:
- Many industries and regions have specific regulations regarding the protection of user data. Implementing robust security measures helps ensure compliance with these regulations, avoiding legal issues and penalties.
- Improving SEO Rankings:
- Search engines prioritize secure websites in their rankings. Implementing security features, such as HTTPS, can positively impact your website’s SEO, leading to better visibility and traffic. Google heavily favors SSL-protected encrypted sites and pushes them higher in search rankings than those without, helping your business become more visible to new potential customers. And not only does our Content Delivery Network (CDN) help protect your site from DDoS attacks, but it also boosts your site’s load time by up to 50% by putting your content on multiple servers around the world, so it’s always close to your customers.
- Mitigating Financial Losses:
- Security breaches can result in significant financial losses, including the costs of fixing the breach, legal expenses, and damage to the brand’s reputation. Investing in security measures is a proactive approach to avoid such financial implications.
- Enhancing User Experience:
- A secure website provides a smoother and more reliable experience for users. Users are more likely to engage with and return to a website that they trust to keep their information safe.
- Protecting Against Phishing Attacks:
- Website security measures help prevent phishing attacks, where malicious actors attempt to trick users into providing sensitive information. This protects both the website and its users from falling victim to fraudulent activities. Take a proactive, preventative approach to the safety of your website. The Website Security firewall helps block attacks on your site while its malware scanner regularly searches your site for malicious content and alerts you if any is found.
-
Website backup with one-click restore.
With Advanced and Premium Plans, get daily, automatic backups** of your website. One-click restore lets you reinstate a clean version of your website with just a single click.
Kathleen’s customers continue to browse her site, safely and without interruption, as website security keeps scanning in the background. Kathleen gets back to business without any downtime. Her customers stay safe and her reputation stays golden.
Website Security FAQs
What makes Website Security so simple?
Where can I find my SSL Certificate?
If I have an SSL Certificate, do I still need Website Security?
Yes — while an SSL certificate encrypts data being transmitted to and from your website, it doesn’t protect your site from other vulnerabilities, such as malware, SQL injections or DDoS attacks. By utilizing both an SSL and Website Security, you are taking steps to help protect more aspects of your site.

